Reason:KubeletNotReady Message:PLEG is not healthy
Kubernetes集群使用CentOS 7.6版本的系统时,如果你的 node 突然 notready,或者 pod状态异常时,kubelet日志中可能存在以下告警信息。
Reason:KubeletNotReady Message:PLEG is not healthy:
PLEG is not healthy: pleg was last seen active 3m5.30015447s ago;
什么是 PLE?
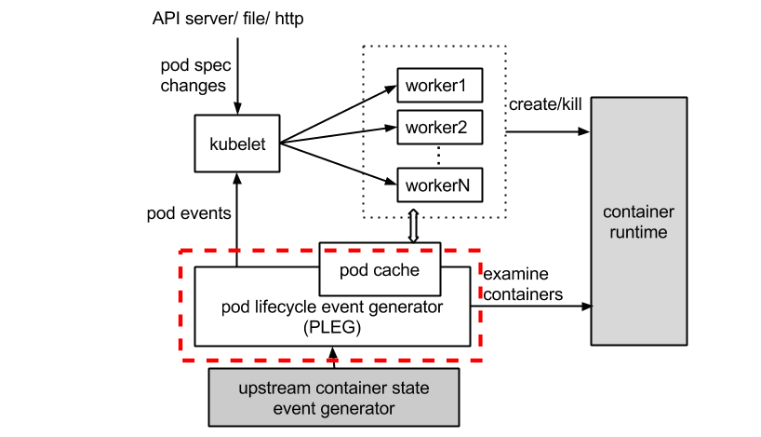
PLEG:全称是Pod Lifecycle Event Generator,主要负责将Pod级事件调整容器运行时状态变化记录event以及触发Pod同步
“PLEG不健康”是怎么发生的?
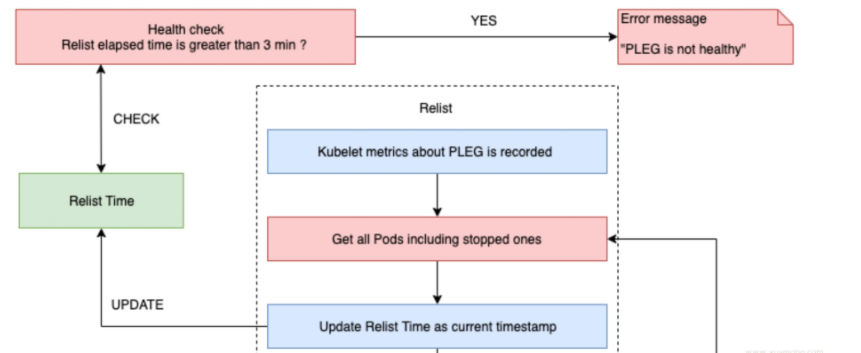
Kubelet 通过以下方式Healthy()定期调用来持续检查 PLEG 健康状况SyncLoop()。
Healthy()检查relist进程(PLEG 关键任务)是否在 3 分钟内完成。此函数被添加runtimeState为“PLEG”,并从“SyncLoop”定期调用(默认为每 10 秒)。如果“重新列出”过程花费的时间超过 3 分钟,则会通过此堆栈过程报告“PLEG 不健康”问题。

//// pkg/kubelet/pleg/generic.go - Healthy()
// The threshold needs to be greater than the relisting period + the
// relisting time, which can vary significantly. Set a conservative
// threshold to avoid flipping between healthy and unhealthy.
relistThreshold = 3 * time.Minute
:
func (g *GenericPLEG) Healthy() (bool, error) {
relistTime := g.getRelistTime()
elapsed := g.clock.Since(relistTime)
if elapsed > relistThreshold {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg was last seen active %v ago; threshold is %v", elapsed, relistThreshold)
}
return true, nil
}
//// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go - NewMainKubelet()
func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, ...
:
klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy)
//// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go - syncLoop()
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
:
// The resyncTicker wakes up kubelet to checks if there are any pod workers
// that need to be sync'd. A one-second period is sufficient because the
// sync interval is defaulted to 10s.
:
const (
base = 100 * time.Millisecond
max = 5 * time.Second
factor = 2
)
duration := base
for {
if rs := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); len(rs) != 0 {
glog.Infof("skipping pod synchronization - %v", rs)
// exponential backoff
time.Sleep(duration)
duration = time.Duration(math.Min(float64(max), factor*float64(duration)))
continue
}
:
}
:
}
//// pkg/kubelet/runtime.go - runtimeErrors()
func (s *runtimeState) runtimeErrors() []string {
:
for _, hc := range s.healthChecks {
if ok, err := hc.fn(); !ok {
ret = append(ret, fmt.Sprintf("%s is not healthy: %v", hc.name, err))
}
}
:
}
以node notready 这个场景为例:
Kubelet中的NodeStatus机制会定期检查集群节点状况,并把节点状况同步到API Server。而NodeStatus判断节点就绪状况的一个主要依据,就是PLEG。
PLEG定期检查节点上Pod运行情况,并且会把pod 的变化包装成Event发送给Kubelet的主同步机制syncLoop去处理。但是,在PLEG的Pod检查机制不能定期执行的时候,NodeStatus机制就会认为这个节点的状况是不对的,从而把这种状况同步到API Server,我们就会看到 not ready
PLEG有两个关键的时间参数,一个是检查的执行间隔,另外一个是检查的超时时间。以默认情况为准,PLEG检查会间隔一秒,换句话说,每一次检查过程执行之后,PLEG会等待一秒钟,然后进行下一次检查;而每一次检查的超时时间是三分钟,如果一次PLEG检查操作不能在三分钟内完成,那么这个状况,会被NodeStatus机制当做集群节点NotReady的凭据,同步给API Server。
如下图,上边一行表示正常情况下PLEG的执行流程,下边一行则表示有问题的情况。relist是检查的主函数。
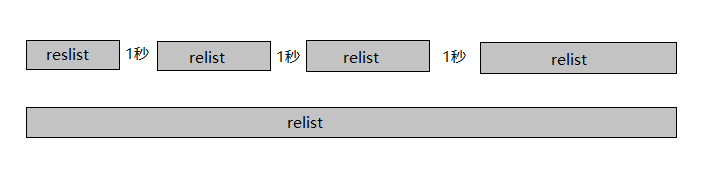
PLEG Start就是启动一个协程,每个relistPeriod(1s)就调用一次relist,根据最新的PodStatus生成PodLiftCycleEvent。
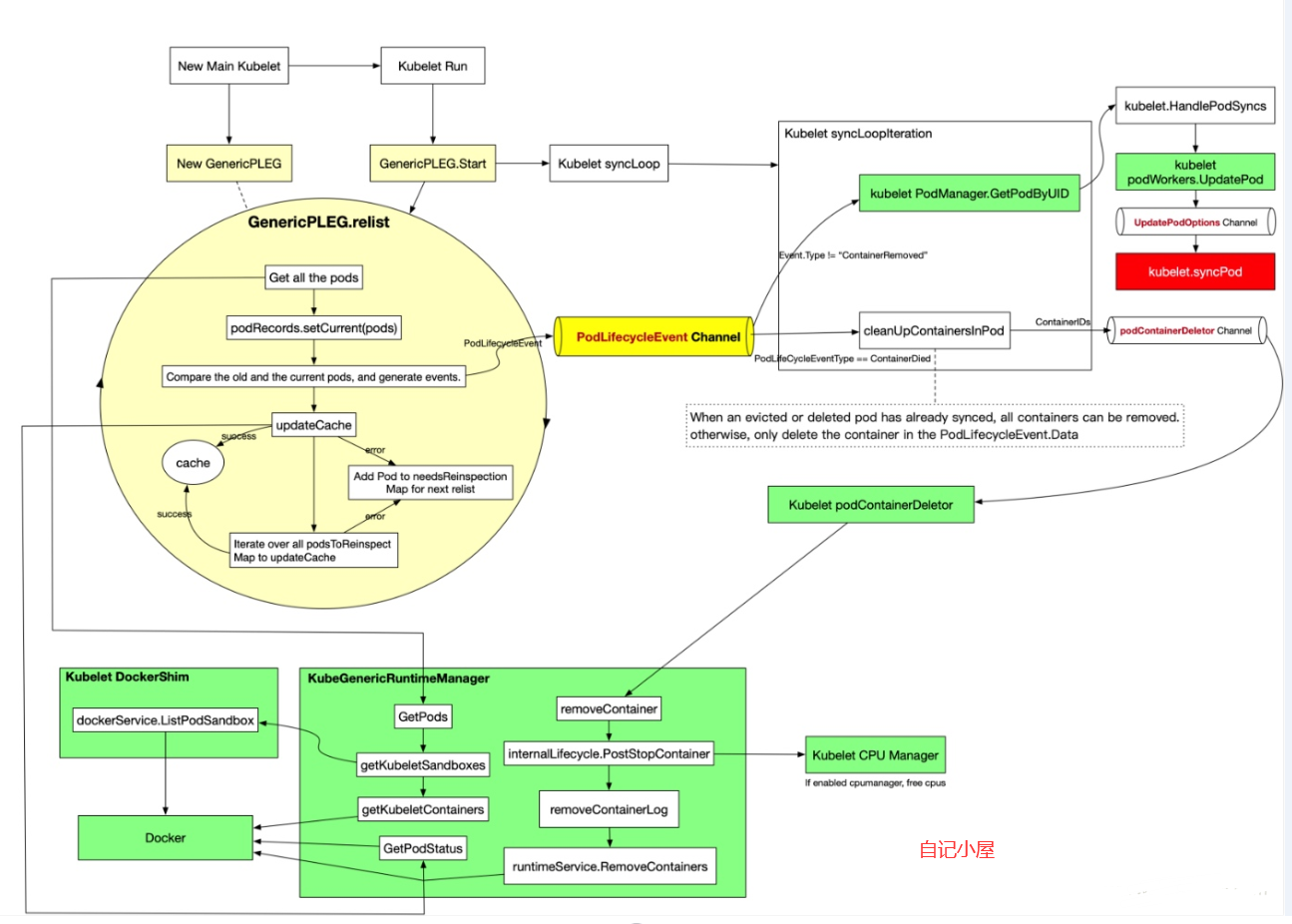
relist是PLEG的核心,它从container runtime中查询属于kubelet管理的containers/sandboxes的信息,并与自身维护的 pods cache 信息进行对比,生成对应的 PodLifecycleEvent,然后输出到 eventChannel 中,通过 eventChannel 发送到 kubelet syncLoop 进行消费,然后由 kubelet syncPod 来触发 pod 同步处理过程,最终达到用户的期望状态。
not healthy 是如何发生的:
Healthy() 函数会以 “PLEG” 的形式添加到 runtimeState 中,Kubelet 在一个同步循环(SyncLoop() 函数)中会定期(默认是 10s)调用 Healthy() 函数。Healthy() 函数会检查 relist 进程(PLEG 的关键任务)是否在 3 分钟内完成。如果 relist 进程的完成时间超过了 3 分钟,就会报告 PLEG is not healthy。
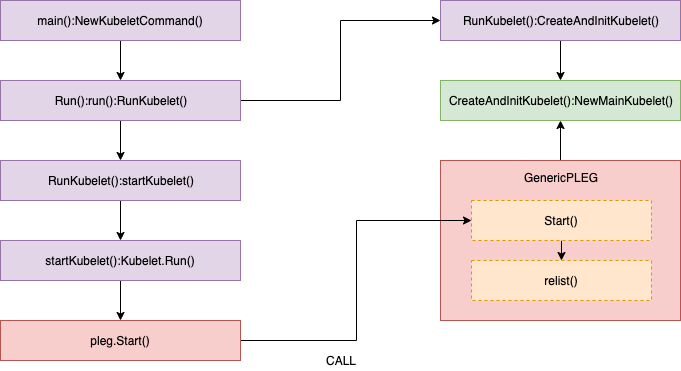
主要逻辑:
//// pkg/kubelet/pleg/generic.go - Healthy()
relistThreshold = 3 * time.Minute
:
func (g *GenericPLEG) Healthy() (bool, error) {
relistTime := g.getRelistTime()
elapsed := g.clock.Since(relistTime)
if elapsed > relistThreshold {
return false, fmt.Errorf("pleg was last seen active %v ago; threshold is %v", elapsed, relistThreshold)
}
return true, nil
}
//// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go - NewMainKubelet()
func NewMainKubelet(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, ...
:
klet.runtimeState.addHealthCheck("PLEG", klet.pleg.Healthy)
//// pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go - syncLoop()
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
:
// The resyncTicker wakes up kubelet to checks if there are any pod workers
// that need to be sync'd. A one-second period is sufficient because the
// sync interval is defaulted to 10s.
:
const (
base = 100 * time.Millisecond
max = 5 * time.Second
factor = 2
)
duration := base
for {
if rs := kl.runtimeState.runtimeErrors(); len(rs) != 0 {
glog.Infof("skipping pod synchronization - %v", rs)
// exponential backoff
time.Sleep(duration)
duration = time.Duration(math.Min(float64(max), factor*float64(duration)))
continue
}
:
}
:
}
//// pkg/kubelet/runtime.go - runtimeErrors()
func (s *runtimeState) runtimeErrors() []string {
:
for _, hc := range s.healthChecks {
if ok, err := hc.fn(); !ok {
ret = append(ret, fmt.Sprintf("%s is not healthy: %v", hc.name, err))
}
}
:
}
relist 处理
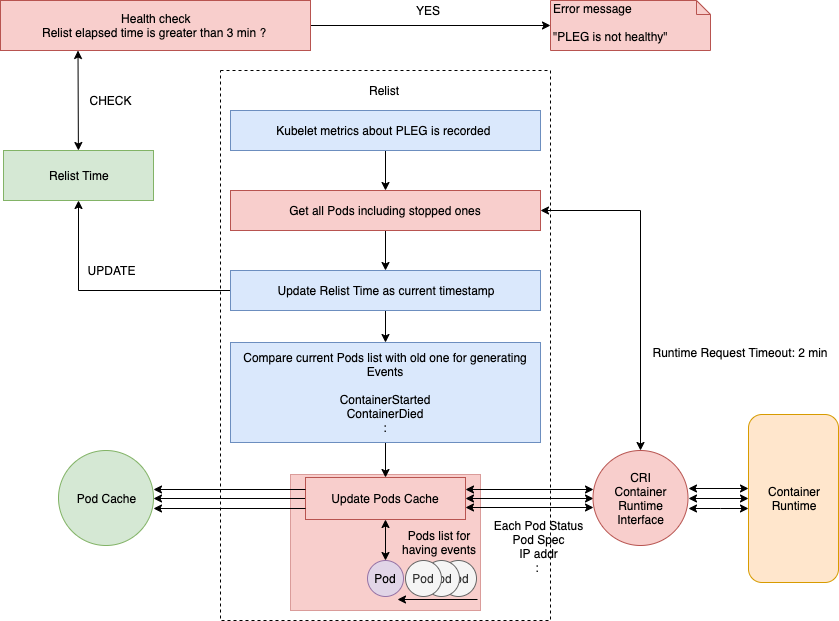
即使将relist设置为每1秒调用一次,如果容器运行时响应缓慢,或者一个周期中发生许多容器更改时,也可能需要花费1秒以上的时间才能完成。因此,下一个relist将在上一个完成后调用。
例如,如果relist需要5秒才能完成,则下一次relist时间为6秒(1秒+ 5秒)
因此如果容器数量很大或者进程有问题,会出现延时,3 分钟内没有响应,就会出现not healthy ,因此监控relist的延迟是有必要的,kubelet 暴露了和 pleg 相关的指标,可以通过这些指标查看当前的状态
relist周期为1秒,换言之重新提交完整的时间(kubelet_pleg_relist_latency_microseconds)+ 1秒kubelet_pleg_relist_interval_microseconds。此外,您可以监控每个操作在容器运行时需要多长时间。这些指标也有助于故障排除。
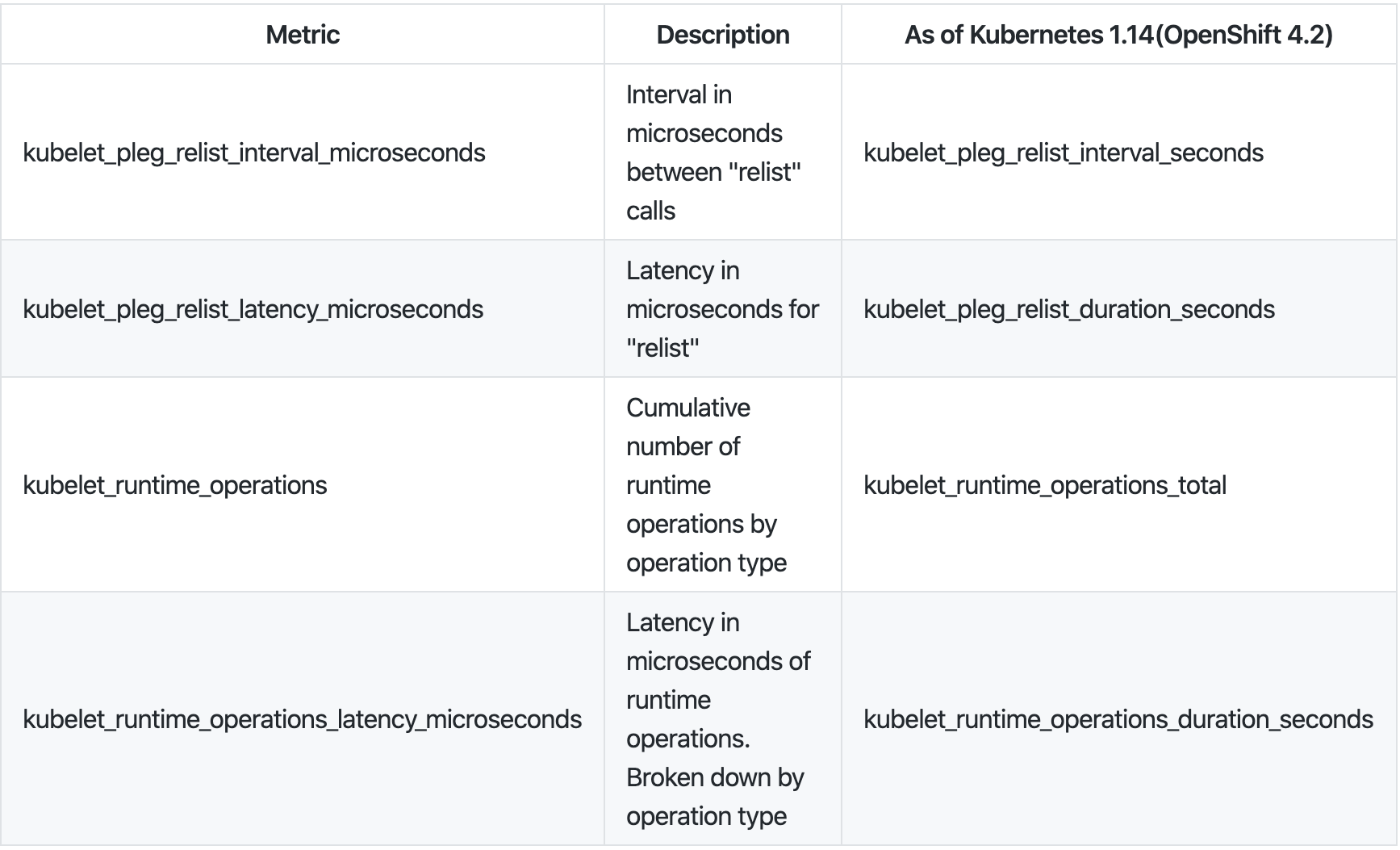
relist 指标监控:
//// pkg/kubelet/pleg/generic.go - relist()
:
// get a current timestamp
timestamp := g.clock.Now()
// kubelet_pleg_relist_latency_microseconds for prometheus metrics
defer func() {
metrics.PLEGRelistLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(timestamp))
}()
// Get all the pods.
podList, err := g.runtime.GetPods(true)
:
最后,updateCache()将检查每个Pod,并在一个循环中一个接一个地更新它,因此,如果在同一relist期间更改了许多Pod ,则此过程可能会成为瓶颈。然后新Pod生命周期事件将发送到eventChannel。
for pid, events := range eventsByPodID {
pod := g.podRecords.getCurrent(pid)
if g.cacheEnabled() {
// updateCache() will inspect the pod and update the cache. If an
// error occurs during the inspection, we want PLEG to retry again
// in the next relist. To achieve this, we do not update the
// associated podRecord of the pod, so that the change will be
// detect again in the next relist.
// TODO: If many pods changed during the same relist period,
// inspecting the pod and getting the PodStatus to update the cache
// serially may take a while. We should be aware of this and
// parallelize if needed.
if err := g.updateCache(pod, pid); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("PLEG: Ignoring events for pod %s/%s: %v", pod.Name, pod.Namespace, err)
:
}
:
}
// Update the internal storage and send out the events.
g.podRecords.update(pid)
for i := range events {
// Filter out events that are not reliable and no other components use yet.
if events[i].Type == ContainerChanged {
continue
}
g.eventChannel <- events[i]
}
}
排查
出现 pleg not healthy,一般有以下几种可能:
- 容器运行时无响应或响应超时,如 docker进程响应超时(比较常见)
- 该节点上容器数量过多,导致 relist 的过程无法在 3 分钟内完成
- relist 出现了死锁,该 bug 已在 Kubernetes 1.14 中修复。
- 网络
docker进程hang 死导致 pleg遇到过很多次,一般是由于 docker 版本过旧,或者机器负载过高导致,可以把 kubelet和 docker 的日志等级调到最高,对比日志定位后进行处理
解决方案
在Kubernetes集群的各节点上执行以下命令,更新systemd程序包至最新版本并重新运行systemd程序。
yum update -y systemd && systemctl daemon-reexec